 Java Online Training In Andhra Pradesh and Telangana
Java Online Training In Andhra Pradesh and Telangana  9010519704
9010519704
Opening Hours :7AM to 9PM
Java Datatypes
Datatypes
Datatypes are used to identify the type of data or which allocates the sufficient memory space for the Variable.These Datatypes are classified into following types:
1.Primitive Datatypes
2.Derived Datatypes
3.User Defined Datatypes
Primitive Datatypes:
Primitive datatypes are used to store the single value at a timeExample:
int x=10;
int y=10,20;(invalid)
These Primitive datatypes are classified into following types
1.Integer Datatype
2.Floating Point Datatype
3.Character Datatype
4.Boolean Datatype
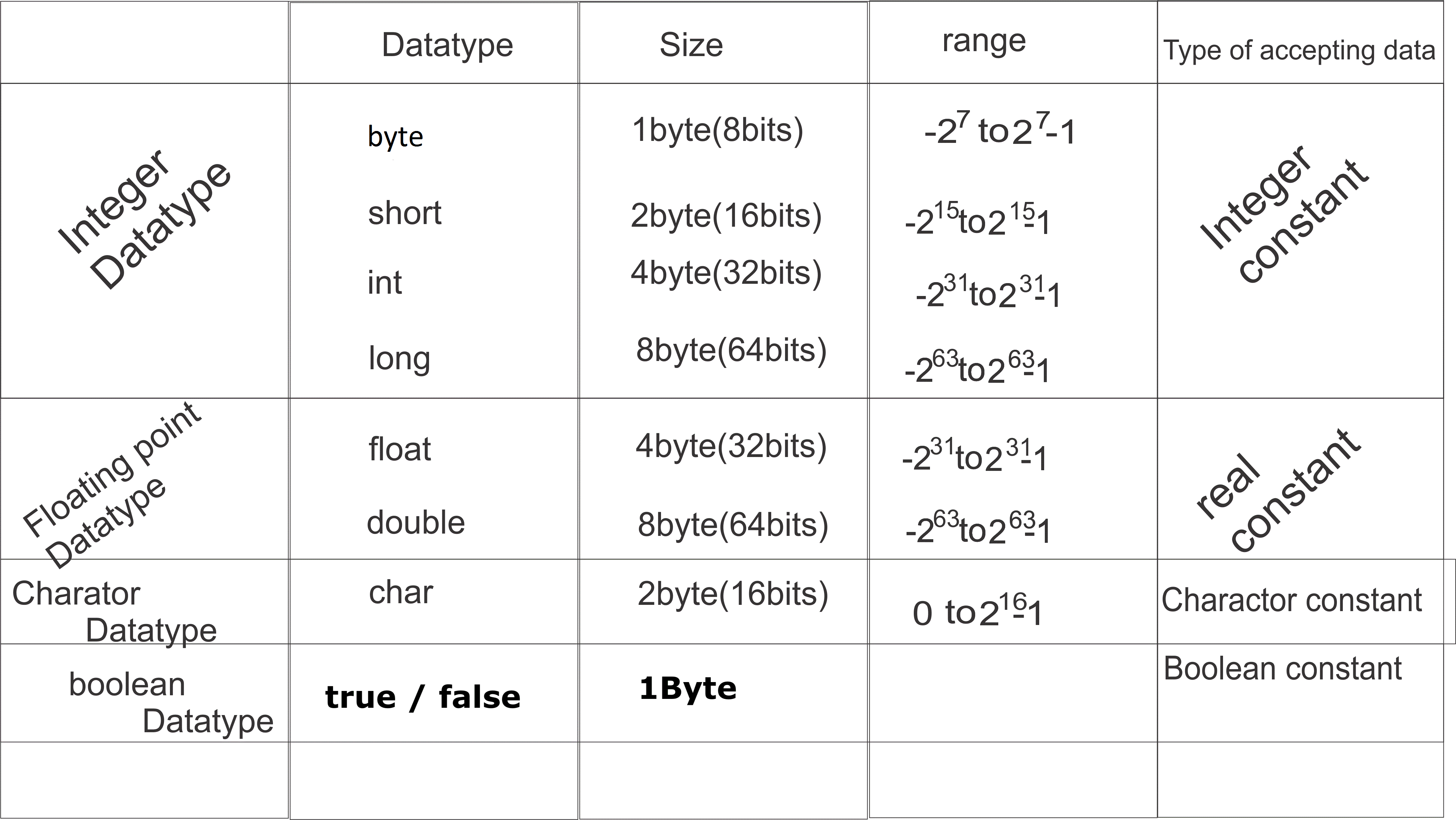 Note: In C-language character datatype occupies one byte of memory because it supports ASCII code(American Standard Code for Information Interchange ).It contains 256 characters only.
Note: In C-language character datatype occupies one byte of memory because it supports ASCII code(American Standard Code for Information Interchange ).It contains 256 characters only. So character datatype occupies one byte of memory.
In java language character datatype occupies two bytes of memory because it supports UNI Code(Universal Coding System).It contains 18 international languages.each language contains their own alphabets and symbols and numbers.Each characters contains one unique value.So java language character datatype occupies 2 bytes of memory
ASCII Codes:
A- 65
a- 97
0-48
Derived Datatypes:
These are used to store the more than one value similar typeExample:
Arrays
int marks[]={10,20,30,40,50}
char x[]={'a','b','c','d'}
User Defined Datatypes:
These are used to store the more than one value dissimilar typeExample:
class
class Demo
{
int x;
float y;
char z;
}
